.1*s=
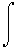 0 to C0-10%(ds/dnp)dnp
(ds/dnp)dnp
0 to C0-10%(ds/dnp)dnp
(ds/dnp)dnpetc... Where
s=
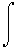 all Np(ds/dnp)dnp
all Np(ds/dnp)dnpThe average number of participants where simultaneously found over these ranges using
Npa=(1/A)
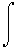 Np*(ds/dNp)*dNp
Np*(ds/dNp)*dNpwhere
A=
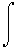 (ds/dNp)*dNp
(ds/dNp)*dNpFor 200 Gev, Sigma NN=5.341 (average of Regge theory and CHC fit)
| 0-10% | 10-30% | 30-50% | 50-70% | |
| Np average | 326.3 | 202.2 | 98.3 | 39.3 |
| Np end | 276 | 141 | 63 | 21 |
| Nch/Np | 1.54 | 1.54 | 1.54 | 1.54 |
| Nch average | 502.5 | 311.4 | 151.4 | 60.5 |
| Nch end | 425 | 217 | 97 | 32 |
For 20 Gev, Sigma NN=3.89 (average of Regge theory and CHC fit)
(The last row is the cutoffs used in the 20 Gev analysis, for comparison)
| 0-10% | 10-30% | 30-50% | 50-70% | |
| Np average | 317.9 | 192.3 | 90.8 | 35.5 |
| Np end | 266 | 132 | 57 | 19 |
| Nch/Np | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 |
| Nch average | 276.6 | 167.3 | 79.0 | 30.9 |
| Nch end | 231 | 115 | 50 | 17 |
| Analysis Nch end | 237 | 117 | 48 | 14 |
This method agreed fairly well wih the cutoffs already used.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bigger tables for 20 and 200 GeV
Experimental data:
| Np end | Nch end | Np average | Nch average | b average | |
| 0-5% | 332 | 289 | 357 | 311 | 1.3 |
| 5-10% | 291 | 253 | 311 | 271 | 3.1 |
| 10-20% | 205 | 178 | 248 | 216 | 4.7 |
| 20-30% | 140 | 122 | 169 | 147 | 6.7 |
| 30-40% | 101 | 88 | 119 | 104 | 8.0 |
| 40-50% | 74.7 | 65 | 87.3 | 76.0 | 8.9 |
| 50-60% | 54.0 | 47 | 63.8 | 55.5 | 9.8 |
| 60-70% | 39.1 | 34 | 46.2 | 40.2 | 10.4 |
| 70-80% | 27.6 | 24 | 33.0 | 28.7 | 11.0 |
| 80-100% | 4.60 | 4 | 16.7 | 14.5 | 12.0 |
Nch end and Nch average are calculated directly from the experimental data, Np end and Np average are obtained by multiplying by the proportionality factor a=0.87 where Nch=a*Np. This value of a was obtained from this eyeball fit. b average is obtained from Glauber generated table Np average vs b.
20 gev Glauber data
| Np end | Nch end | Np average | Nch average | b average | |
| 0-5% | 316 | 275 | 347 | 302 | 1.8 |
| 5-10% | 267 | 232 | 291 | 253 | 3.6 |
| 10-20% | 190 | 165 | 226 | 197 | 5.3 |
| 20-30% | 133 | 115 | 160 | 139 | 6.9 |
| 30-40% | 90 | 78.3 | 110 | 95.7 | 8.3 |
| 40-50% | 58 | 50.5 | 73.1 | 63.6 | 9.4 |
| 50-60% | 35 | 30.5 | 45.8 | 39.8 | 10.5 |
| 60-70% | 19 | 16.5 | 26.3 | 22.9 | 11.4 |
| 70-80% | 10 | 8.70 | 14.0 | 12.2 | 12.2 |
| 80-100% | 2 | 1.74 | 5.06 | 4.40 | 13.2 |
Np end and Np average are calculated directly from the experimental data, Nch end and Nch average are obtained by multiplying by the proportionality factor a=0.87 where Nch=a*Np. This value of a was obtained from this eyeball fit. b average is obtained from Glauber generated table Np average vs b.
200 gev experiment
| Np end | Nch end | Np average | Nch average | b average | |
| 0-5% | 324 | 499 | 353 | 544 | 1.5 |
| 5-10% | 276 | 425 | 299 | 460 | 3.4 |
| 10-20% | 199 | 306 | 236 | 363 | 5.0 |
| 20-30% | 141 | 217 | 169 | 260 | 6.8 |
| 30-40% | 97 | 149 | 118 | 181 | 8.1 |
| 40-50% | 63 | 97.0 | 79.1 | 122 | 9.2 |
| 50-60% | 39 | 60.0 | 50.3 | 77.5 | 10.2 |
| 60-70% | 22 | 33.9 | 29.9 | 46.0 | 11.2 |
| 70-80% | 12 | 18.5 | 16.5 | 25.4 | 12.0 |
| 80-100% | 3 | 4.62 | 6.52 | 10.0 | 13.1 |
Nch end and Nch average are calculated directly from the experimental data, Np end and Np average are obtained by multiplying by the proportionality factor a=1.57 where Nch=a*Np. This value of a was obtained from this eyeball fit. b average is obtained from Glauber generated table Np average vs b.
200 gev Glauber data
| Np end | Nch end | Np average | Nch average | b average | |
| 0-5% | 327 | 503 | 357 | 550 | 1.3 |
| 5-10% | 281 | 432 | 303 | 466 | 3.3 |
| 10-20% | 206 | 317 | 242 | 372 | 4.9 |
| 20-30% | 148 | 228 | 175 | 270 | 6.6 |
| 30-40% | 103 | 158 | 124 | 191 | 7.9 |
| 40-50% | 68.2 | 105 | 84.4 | 130 | 9.1 |
| 50-60% | 42.9 | 66 | 54.8 | 84.4 | 10.1 |
| 60-70% | 24.7 | 38 | 33.1 | 51.0 | 11.0 |
| 70-80% | 13.0 | 20 | 18.3 | 28.2 | 11.9 |
| 80-100% | 1.3 | 2 | 6.2 | 9.55 | 13.1 |